为什么需要 Callable
无论是继承 Thread 类,还是实现 Runnale 接口,或者使用线程池的 execute 方法去执行一个异步任务,都无法将这个任务的返回值带出来,以 Runnale 接口为例:
/**
* @since JDK1.0
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
可以看到 run() 方法没有参数,没有返回值,没有抛出异常,因此不能适用于那些需要异步任务返回值得场景,由此就诞生了可以获取异步任务结果的工具: Callable
Callable
又是 Doug Lea 大师
/**
* @see Executor
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> the result type of method {@code call}
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {
V call() throws Exception;
}
Callable 是一个泛型接口,里面只有一个方法,call(), 可以返回泛型值V, Cacheable 与 Runnable 接口很是相似,下面看一下他们之间的区别
Callable VS Runnable
两个接口都是用于多线程执行任务的,但是他们的使用场景的差别还是很大的。
执行机制上的差别
Runnable 可以用在Thread类中,也可以在 ExecutorService 中配合线程池使用,但是 Callable 只能用于 ExecutorService 中,Thread 类中没有 Cacheable 的身影:
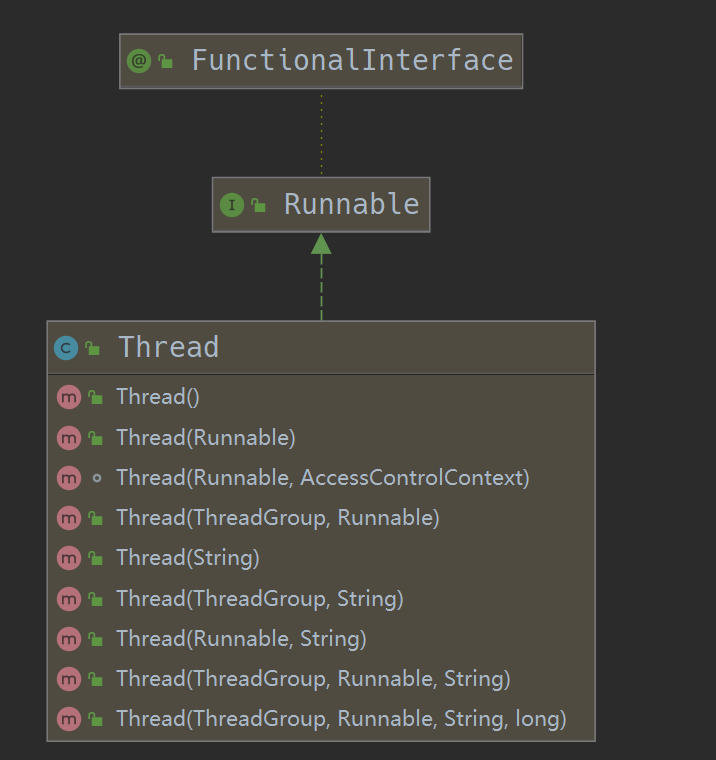
异常处理的差别
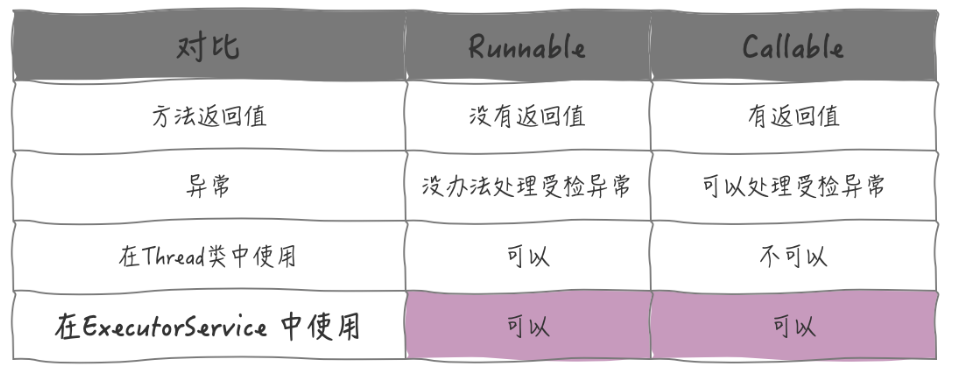
Runnable 接口中的 run 方法签名上没有 throws, 自然也不能向上传播受检异常。而 Callable 接口中的 call f方法可以向上抛出异常。
区别总结如下:
Callable 在线程池中的应用
上面说过,Callable 接口只能在 ExecutorService 中使用,下面看一下如何使用的
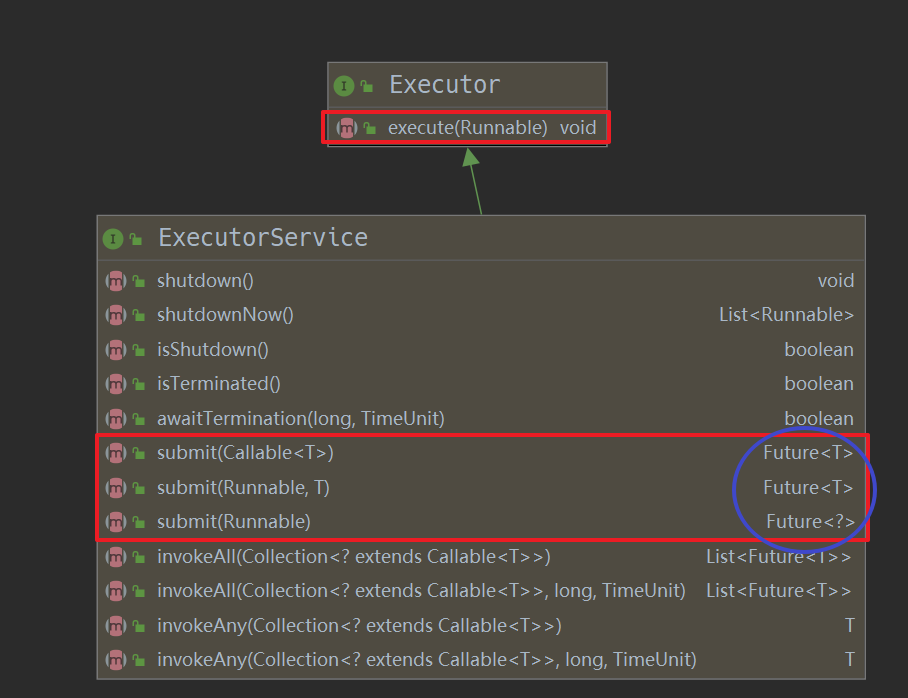
可以看到在 submit 方法中可以接收一个实现了 Callable 接口的任务, 返回的是 Future 类型。而 execute 方法无返回值。 那么 Future 是什么呢? 如何通过 Future 拿到返回值呢?
Future
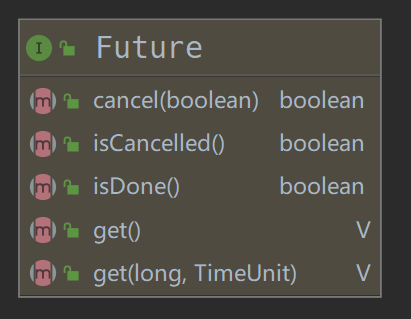
Future 是一个接口,通过方法名就可以看出他们的用途:
// 取消任务
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
// 获取任务执行结果
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
// 获取任务执行结果,带有超时时间限制
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
// 判断任务是否已经取消
boolean isCancelled();
// 判断任务是否已经结束
boolean isDone();
看一下如何使用:
public class FutureDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 使用 Callable ,可以获取返回值
Callable<String> callable = () -> {
System.out.println("进入 Callable 的 call 方法");
// 模拟子线程任务,在此睡眠 2s,
// 小细节:由于 call 方法会抛出 Exception,这里不用像使用 Runnable 的run 方法那样 try/catch 了
Thread.sleep(5000);
return "Hello from Callable";
};
System.out.println("提交 Callable 到线程池");
Future<String> future = executorService.submit(callable);
System.out.println("主线程继续执行");
System.out.println("主线程等待获取 Future 结果");
// //检查任务是否做完
// while(!future.isDone()) {
// System.out.println("Task is still not done...");
// Thread.sleep(1000);
// }
// Future.get() blocks until the result is available
String result = future.get();
System.out.println("主线程获取到 Future 结果: " + result);
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
结果如下:
提交 Callable 到线程池
主线程继续执行
主线程等待获取 Future 结果
进入 Callable 的 call 方法
主线程获取到 Future 结果: Hello from Callable
Process finished with exit code 0
如果子程序运行时间过长,或者其他原因,我们想 cancel 子程序的运行,则我们可以使用 Future 提供的 cancel 方法,继续对程序做一些修改
while(!future.isDone()) {
System.out.println("子线程任务还没有结束...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
double elapsedTimeInSec = (System.nanoTime() - startTime)/1000000000.0;
// 如果程序运行时间大于 1s,则取消子线程的运行
if(elapsedTimeInSec > 1) {
future.cancel(true);
}
}
特别注意的是,如果使用 cancel 方法取消了任务, get() 方法会抛出一个 CancellationException 异常。
到这里已经知道和配合使用 Cacheable 和 Future 来获取异步任务的返回值了。总结就只有3点:
- 待执行的任务要实现 Callable 接口中的
- 使用线程池中的submit 方法
- 通过 Future 获取任务的返回值
刚刚我们看 ExecutorService 中的 submit 方法返回的是 Future 接口,然后通过接口中的get 方法获取任务的返回值,其实 submit 返回的是 Future 的实现类: FutureTask, 至于 FutureTask 是如何配合线程池拿到任务的返回值,就需要深入源码查看底层实现了,这个以后再新写一遍博客讲解。