这个封装程序使用的结构和之前分析JSON时使用的结构是相同的。
- 程序首先会创建一些结构,然后通过调用MarshalIndent函数将结构封装为由字节切片组成的JSON数据
- 最后,程序会将封装所得的JSON数据存储到指定的文件中。
也可以通过编码器手动将Go结构编码为json数据
流程如下:
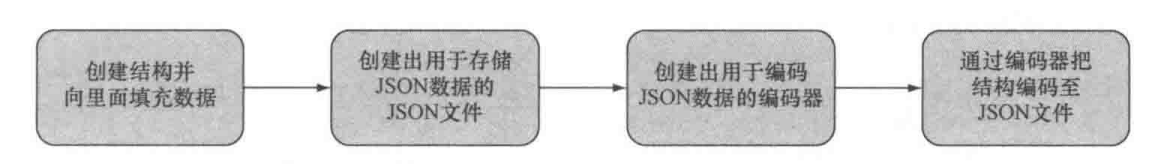
示例
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"os"
)
type Post struct {
// 处理对象属性与json字段的映射关系
// 如果对象属性与json字段名称相同。可以省略
Id int `json:"id"`
Content string `json:"content"`
Author Author `json:"author"`
Comments []Comment `json:"comments"`
}
type Author struct {
Id int `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
}
type Comment struct {
Id int `json:"id"`
Content string `json:"content"`
Author string `json:"author"`
}
func main(){
post := Post{
Id: 1,
Content: "Hello World",
Author: Author{
Id: 2,
Name: "dc1",
},
Comments: []Comment{
{
Id: 3,
Content: "Have a great day",
Author: "Adam",
},
{
Id: 4,
Content: "How are you today",
Author: "Betty",
},
},
}
fmt.Printf("post: %v\n", post)
// 将 json 结构封装为由字节切片组成的Json数据
output, err := json.MarshalIndent(&post,"","\t\t")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// 将数据写入文件中
err = ioutil.WriteFile("post.json",output,0666)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// 使用Encoder将结构编码到文件中
// 创建用于储存json的文件
jsonFile, err := os.Create("./post1.json")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// 创建解码器
encoder := json.NewEncoder(jsonFile)
// 把结构编码到json文件中
err = encoder.Encode(&post)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}